Recent Vision-Language-Action (VLA) models built on pre-trained Vision-Language Models (VLMs) require extensive post-training, resulting in high computational overhead that limits scalability and deployment. Existing sparsification strategies—such as Mixture-of-Depths, layer skipping, and early exit—fall short by neglecting the semantic coupling across vision-language-action modalities, and focusing narrowly on intra-LLM computation while overlooking end-to-end coherence from perception to control. To address these challenges, we propose CogVLA, a Cognition-Aligned Vision-Language-Action framework that leverages instruction-driven routing and sparsification to improve both efficiency and performance. CogVLA draws inspiration from human multimodal coordination and introduces a 3-stage progressive architecture. 1) Encoder-FiLM based Aggregation Routing (EFA-Routing) injects instruction information into the vision encoder to selectively aggregate and compress dual-stream visual tokens, forming a instruction-aware latent representation. 2) Building upon this compact visual encoding, LLM-FiLM based Pruning Routing (LFP-Routing) introduces action intent into the language model by pruning instruction-irrelevant visually grounded tokens, thereby achieving token-level sparsity. 3) To ensure that compressed perception inputs can still support accurate and coherent action generation, we introduce V‑L‑A Coupled Attention (CAtten), which combines causal vision-language attention with bidirectional action parallel decoding. Extensive experiments on the LIBERO benchmark and real-world robotic tasks demonstrate that CogVLA achieves state-of-the-art performance with success rates of 97.4% and 70.0%, respectively, while reducing training costs by 2.5× and decreasing inference latency by 2.8× compared to OpenVLA. CogVLA is open-sourced and publicly available at https://github.com/JiuTian-VL/CogVLA.
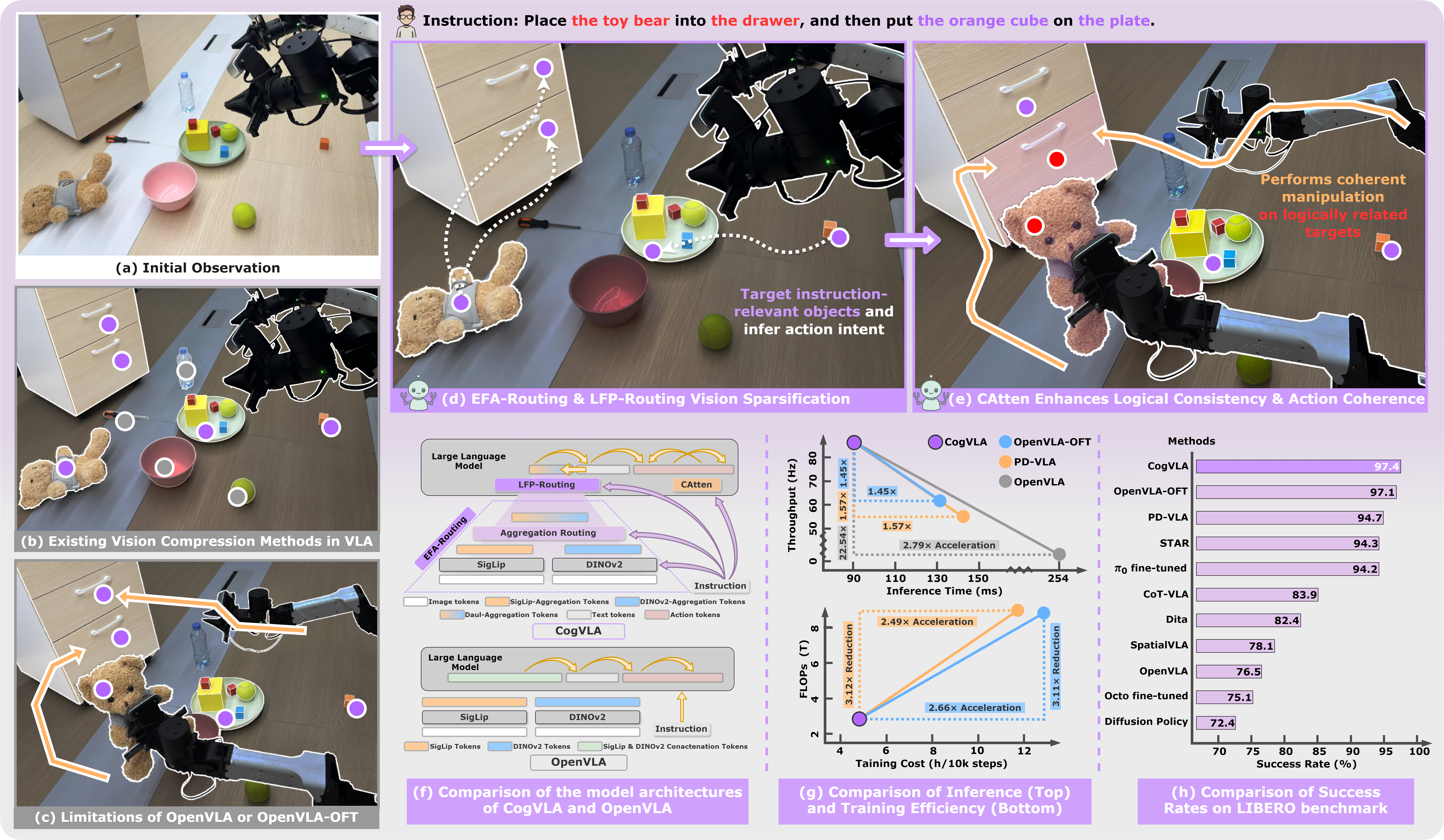
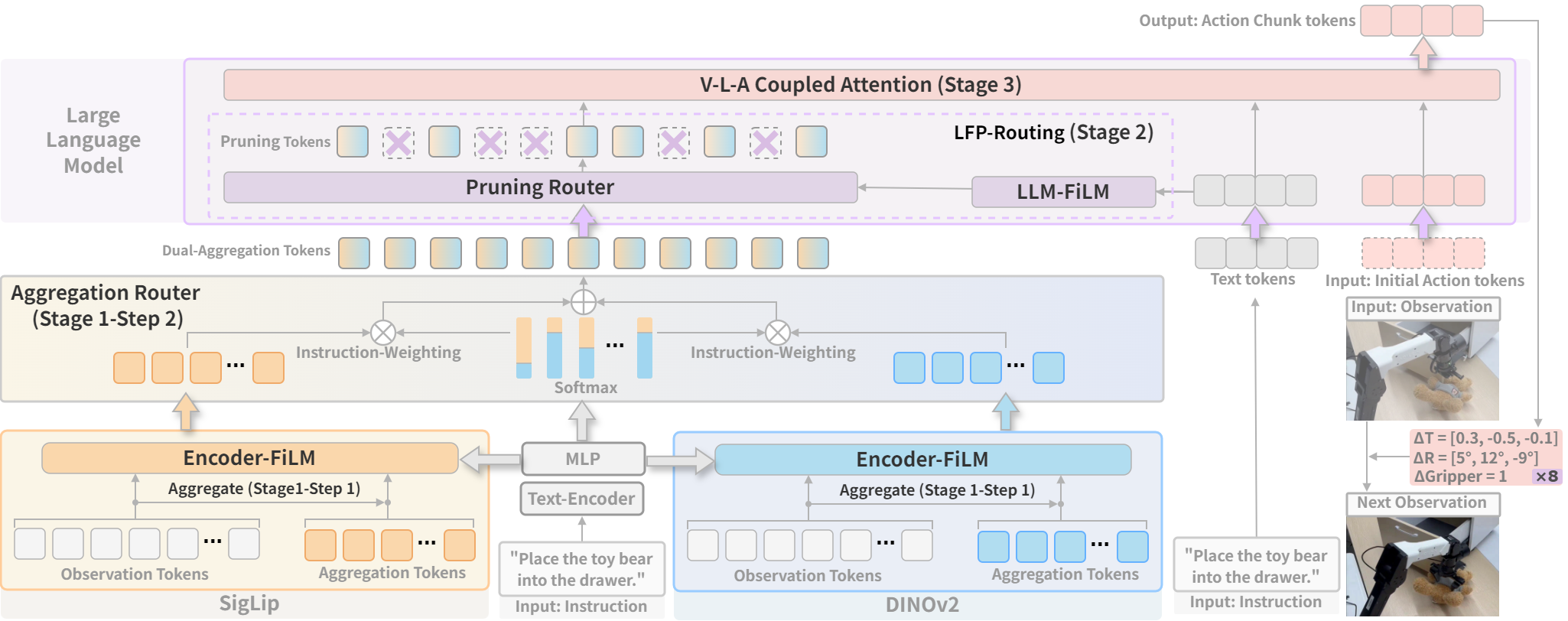
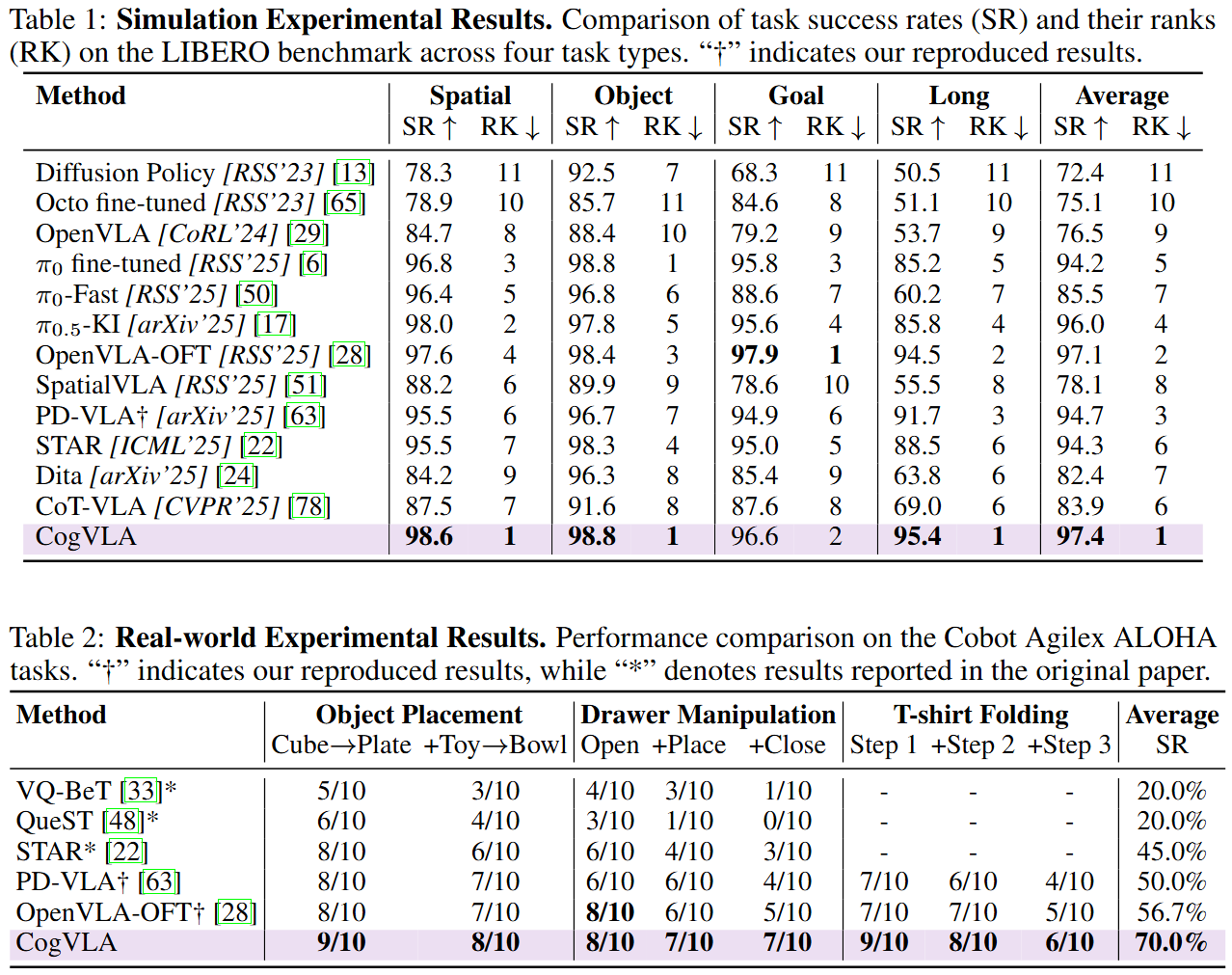
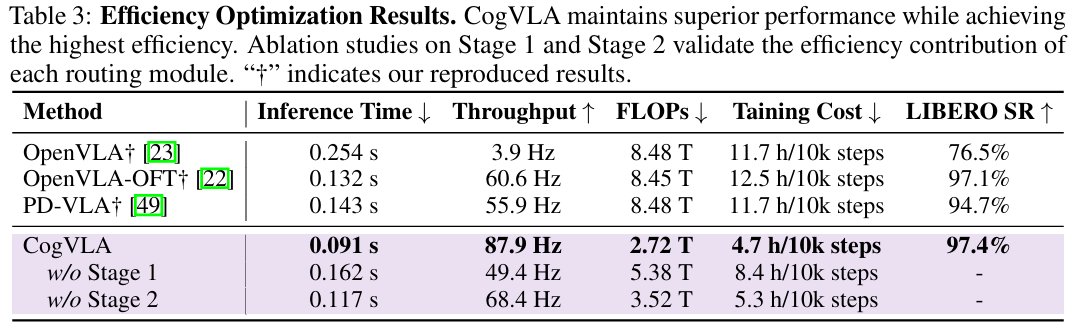
We presented CogVLA, a cognition-aligned and instruction-driven Vision-Language-Action framework designed to address the computational inefficiencies and semantic fragmentation in existing VLA models. By integrating EFA-Routing, LFP-Routing, and CAtten into a unified 3-stage progressive design, CogVLA achieves effective vision sparsification and coherent cross-modal reasoning. Extensive evaluations on both the LIBERO benchmark and real-world robotic tasks demonstrate that CogVLA not only achieves state-of-the-art performance but also significantly reduces computational cost and inference latency. This work highlights the importance of instruction-driven multimodal sparsification in building scalable and efficient embodied AI systems.
@article{li2025cogvla,
title={CogVLA: Cognition-Aligned Vision-Language-Action Model via Instruction-Driven Routing & Sparsification},
author={Li, Wei and Zhang, Renshan and Shao, Rui and He, Jie and Nie, Liqiang},
journal={Advances in neural information processing systems},
year={2025}
}